SSCI-581-Week6
Thinking Geospatially
- Help computer understand what we need!
- Geospatial Data Concepts
- Geospatial Data
- Location and geometry
- Attribute Data
- Information describing the spatial objecets/features
- Cartographic Data
- Symbology and arrangement of the representations
- Geospatial Data
- Reference frameworks
- Datums, projections
- Data Acquisition Systems
- Surveying, GPS
- Data Models
- Raster, Vector
- Functional Models
- Problem-solving
- Information Dissemination
- Visualization, Cartography, Human Interpretation
Geodesy, Datums, and Geographic Coordinate Systems
Geodesy
- The science of measuring and analyzing:
- The size of the Earth
- The shape of the Earth
- Its orientation in space
- Its gravitational field
- Tts magnetic field
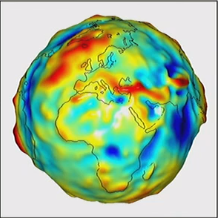
The Gravitational Field
- Knowing the strength of gravity at different places on the surface helps to access the actual shape of the planet
- The geoid is a measured and interpolated surface representing the 3D surface along which the Earth’s gravitational field is constant
- Geoids are now created from satellite measurements and surface readings
- Colors represent deviations from mean sea level
Modeling the Earth
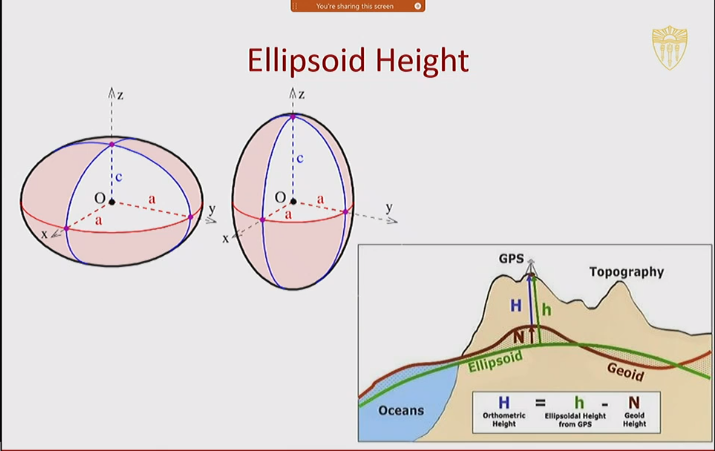
- Spatial data is measured and calculated based on models of the Earth
- Coordinates of Latitude and longitude refer to a shape chosen to represent the earth, not the actual surface
Ellipsoid Height
Datum
- A datum is a mathematical model that standardizes the shape of the Earth for our particular purposes
- A datum is basis for calculating positions on the Earth’s surface
- A datum is composed of three elements:
- An ellipsoid - a surface model of the Earth
- Orientation - the position of the ellipsoid
- Point of origin - the point where the Earth and the ellipsoid align
Horizontal and Vertical Datum
- A horizontal datum standardizes location for horizontal measurements: x,y coordinates
- A vertical datum standardizes elevation and height measurements: Z coordinate
- Horizontal datum can now include a z coordinate, a height measurement from the chosen ellipsoid, but a vertical datum gives a more accurate height measurement
Commonly Used Datum
- NAD27: North American Datum of 1927 (Based on Clarke 1866 ellipsoid)
- NAD83: North American Datum of 1983 (Based on GRS 1980 ellipsoid)
- WGS84: World Geodetic System of 1984 (Based on WGS 1984 ellipsoid)
- Difference up to 250 meters
Choosing a Model (Datum)
- Because the shape of the Earth is not uniform, we must choose on that best represents the Earth for our particular purpose
- We use what we have learned from geodesy to make this choice, including the geoid, surface measurements, satellite imagery, etc.
Coordinate System
Two Kinds of Coordinate Systems
- Geographic Coordinate System (GCS) is locational reference systems based on a graticule over a chosen datum
- Projected Coordinate Systems(PCS) are locational reference systems based on a planar grid - a grid over a 2D surface, and the 2D surface is a chosen projection
The Graticule
- The grid of lines of latitude and longitude
- Latitude
- Lines are parallel to equator
- Describe N/S values
- Longitude
- Lines of meridian converge at poles
- Describes E/W values
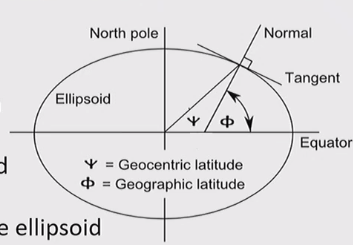
Latitude
- The value of one’s latitude is the angle that a line drawn perpendicular to the surface through a point on a spheroid makes with the equatorial plane - not with center of the ellipsoid
- Called geographic or geodetic latitude
- Positive values in Northern Hemisphere; Negative values in Southern Hemisphere
- Latitude goes to 90 degree
Longitude
- The value of one’s longitude is the angle between the plane of the meridian that passes through a point on the surface of the spheroid and the plane of a chosen prime meridian (where the value of longitude is zero)
- Called geographic or geodetic longitude OR geocentric longitude since the measurement is at the center of the ellipsoid
- Positive values in Eastern Hemisphere
- Negative values in Western Hemisphere
- Longitude goes up to 180 degree
Degrees Minutes and Seconds
- Latitude and Longitude are often expressed in units of Degrees, Minutes, and Second (DMS)
- 1 Degree is broken down into 60 minutes
- 1 Minute is broken down into 60 seconds
- Converting it to Decimal Degrees

Geographic Coordinate Distances

All articles in this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 unless stating additionally.
Comment