Lecture11-Note
Parallel Processing
Algorithmic Complexity
- Linear complexity
- Polynomial complexity
- exponential complexity
Processing Data with a Divide-and-Conquer Strategy
- A Divide-and-Conquer Strategy
- Requires that each piece is independent of the others
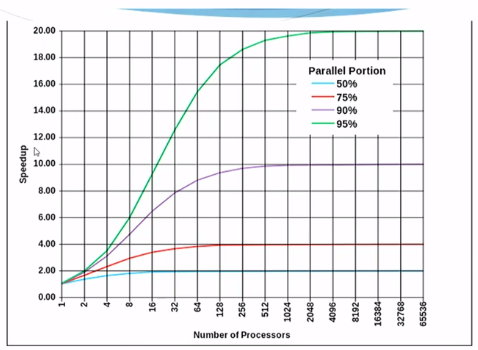
Speedup with Parallel Processing
Critical Path
- A critical path in a computation consists of consecutive steps that are interdependent and therefore not parallelizable
Amdahl’s Law
- The theoretical sppedup in the execution of a task( where p is the proportion of the task that is parallelizable) =
Embarrassingly Parallel Computations
- Embarrassingly parallel tasks are cleanly separable and can be carried out in parallel, typically with significant speedups
Distributed Computing Platforms
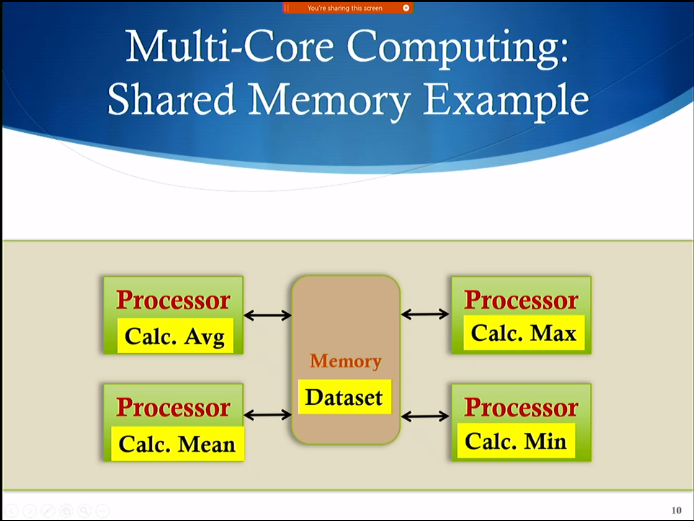
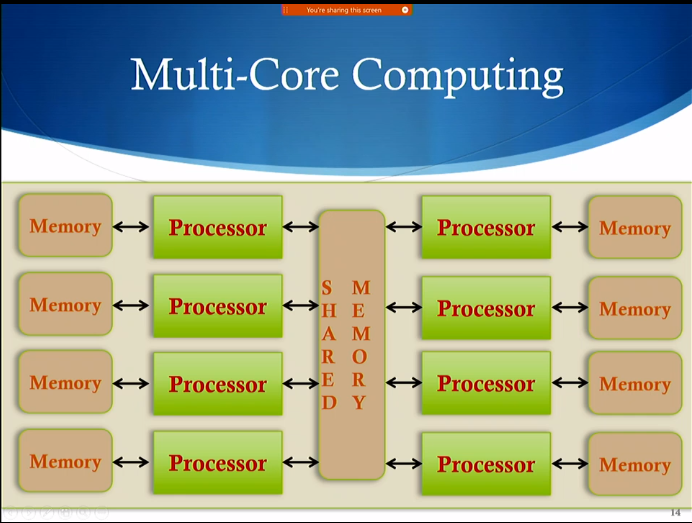
Multi-Core Computing
- Several processors in the same computer
- Sharing memory
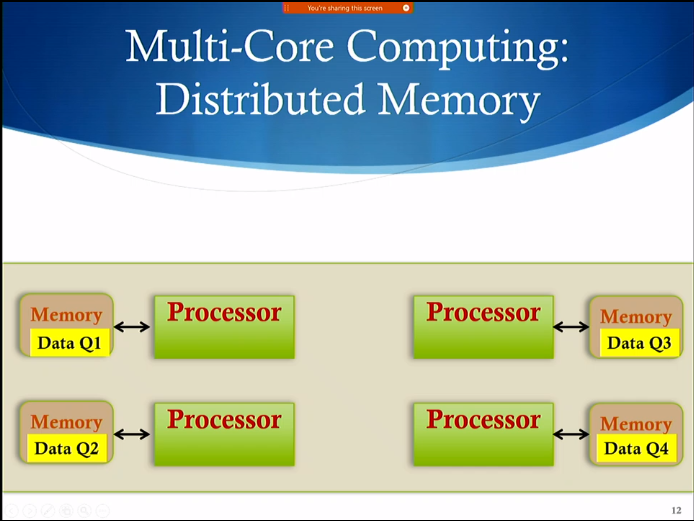
- Distributed Memory
- Mixed-Memory architecture
Graphical Processing Units (GPUs)
- Graphical processing units are designed to do simple computation to display graphics and are very cheap
- They turn out yo be very useful to do simple computations in parallel
Distributed Computing
- A parallel computing paradigm where individual cores do computations that re orchestrated over a network
Different Ways of Distributed Computing
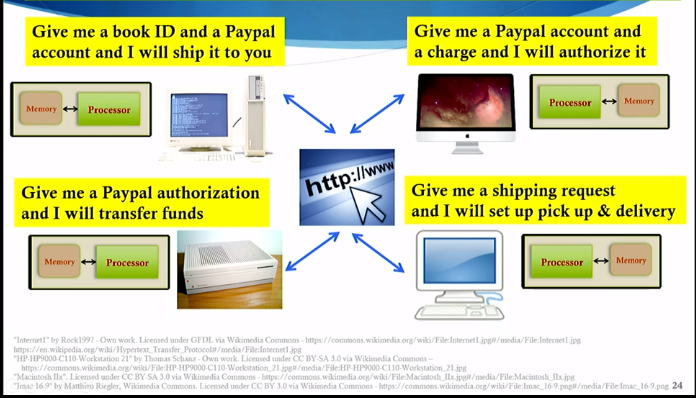
Web Services
- An approach to distributed computing where third parties offer services for remote execution that can be orchestrated to create complex applications
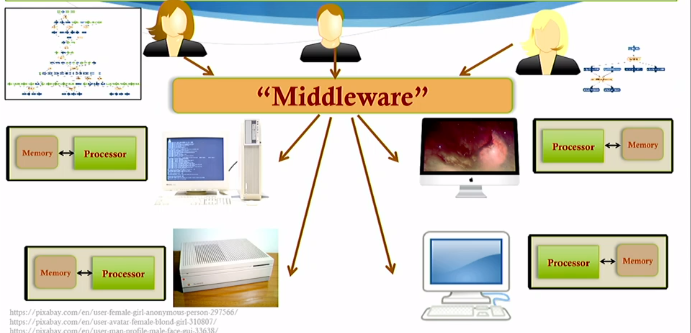
Grid Computing
- An approach to distributed computing where the computing power of several computers of different nature are orchestrated through a central “middleware” control center
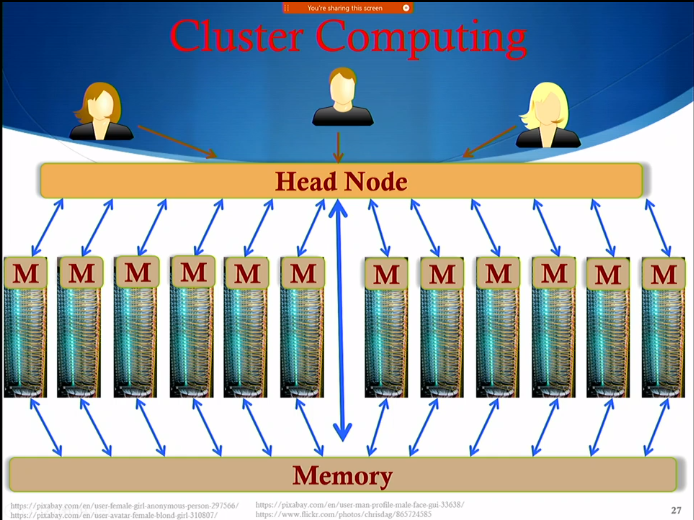
Cluster Computing
- An approach to distributed computing where the precessing power of several computers of very similar nature is orchestrated through a central head node
Cloud Computing Considerations
- Positives:
- No need to purchase computers
- No need for space
- No need to manage computer hardware or software
- Negatives
- Cost of replicating execution environment
- Cost of moving data to the cloud in order to be processed
Virtual Machines
- Virtual machines are frozen versions of all the software in a machine that is needed to run an application, including OS, programming language support, libraries, etc.
Practical Aspects of Distributing Computing
- Execution Failures
- Cooling
- Network Delays
- Queuing Delays
Programming Languages for Distributed Computing
- MapReduce and Hadoop make it possible that many programming languages can be used to give special instructions to use multiple processing and memory units
All articles in this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 unless stating additionally.
Comment