SSCI-581-Week11
Spatial Analysis
What is Spatial Analysis?
-
- A geographical analysis which seeks to explain patterns of human behavior and their spatial expression in terms of mathematics and geometry
-
- The study of “regularities in the spatial distribution of economic activity, populations, land use, and other dimensions of human activity”
Location is Key
- A hugely important determinant of the quality and characteristics of something - an event, a building - is the location
- Being able to identify and analyze characteristics of different locations is a foundational use of GIS and spatial analysis methodologies
Euclidean Distance Buffer
- Straight-line distance; buffer at certain radius from point;
- Ring buffer draws a series of buffers at increasing distances around given features
- Next step in analysis is often to then count how many “things” occur within buffer
Overlay
- Overlay is the layering of data on top of each other in a GIS to analyze multiple aspects of the same location
- It is a fundamental use of a GIS
- There are many different ways to use overlay:
- Intersect
- union
- Subtract
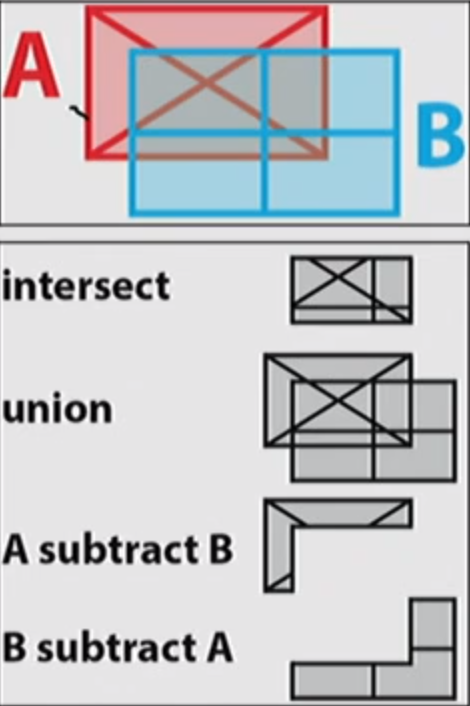
“Crisp” Criteria
- Overlay assumes clarity and crispness of criteria
- Boundaries are definite
- Levels of suitability are clear
- Note in the example that all criteria have specific, crisp definitions and cutoffs
Fuzzy logic and fuzzy membership sets
- Fuzzy logic recognizes that criteria are often not clear or are ill-defined
- Instead of clear criteria definitions and cut-offs, fuzzy logic assumes that a set of suitable choices exists and asks, “What is the likelihood that particular data value is within that suitable set?”
- A fuzzy set replaces original data values with likelihood values. from 0-1
Spatial Patterns:Points Pattern
Spatial Patterns of Data
- Example: A grid of POINT data
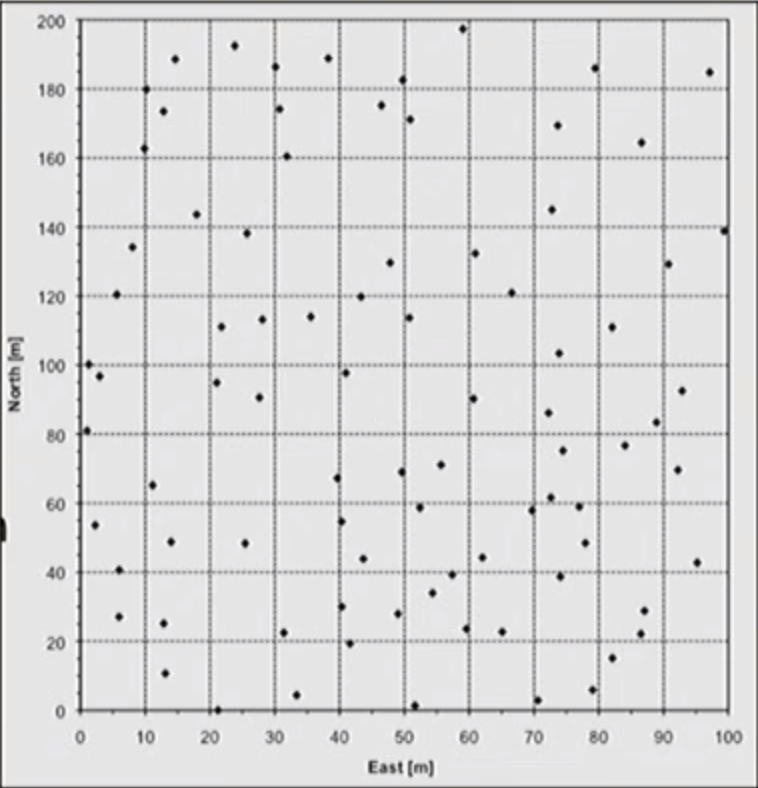
- These could have attribute values we are interested in
- House prices
- Traffic accident counts
- Pollen accounts
- We could be interested in identifying patterns in the event occurrences themselves – the locations (point pattern analysis)
- Or We could be interested in identifying pattern is the values – the ATTRIBUTES (spatial autocorrelation)
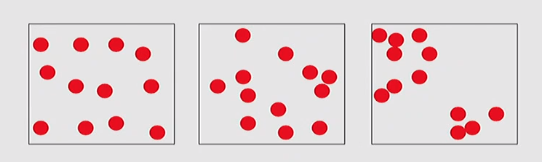
Identify Points Clustered or Not By Sampling Grid
- Normally (ie under randomness) you would expect
- some empty cells
- many with about the mean number of points
- few cells with many points
- Uniform: most have about the average number of points
- Clustered: many empty cells and with many points
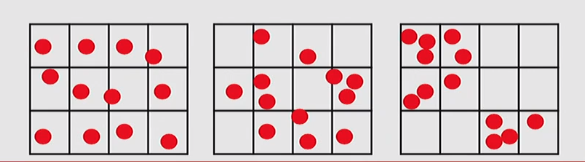
| Deviation | Variance | |
|---|---|---|
| Uniform | small | small |
| Clustered | large | large |
Kernel Estimation
- Kernel estimation uses a kernel function (there are many to choose from) which draws the curve of a mathematical function over each point, and assigns weights to other events found within the search radius based on nearness to the point - thus according to where it sits along the function
- Values for each event within the point’s search radius are summed to give the estimated intensity at the point
- There are better for tackling the areal problem than standard density measure
Average Nearest Neighbor
- A distance-based measure of clustering
- Steps: 1. Measure distance from one point to closest neighboring point 2. repeat for all points; sum distance then divide by number of points
Spatial Patterns: Spatial Autocorrelation
Interpreting Spatial Autocorrelation
-
Null hypothesis is complete spatial randomness
-
Positive spatial autocorrelation: Neighbor locations are more likely to have similar values
-
Negative spatial autocorrelation: Neighbor locations are more likely to have dissimilar values

Hotspot map is relative value.
Spatial Modeling
What is Spatial Model
- A spatial model is
- a representation
- of a real process operating on the Earth’s surface
- a design process conceived of by a human
Relationship to theory
- A Theory
- an abstraction of some phenomena
- A model
- simplification of reality which takes the theoretical abstractions and puts it into a from that we can manipulate
- simulation is often used to characterize this process of implementation
Representation Models and Process Models
- Distinction:
- A representation model is template for data, a framework into which specific details of relevant aspects of the Earth’s surface can be fitted. It is a statement about how the world looks.
- Process models are expressions of how world is believed to work.They are expressions of process.
- Two key requirements of spatial process models:
- There is variation across the space being manipulated by the model
- The results of modeling change when locations of objects change
Methods for Process Models
- Analytical: use mathematical analysis to arrive at explicit equations representing the behavior of the system
- Simulation: used to derive the behavior of the system when it is too complex to be modeled via analytical approach
Species Distribution Models
-
Utilizes known species occurrence and environmental variables to predict occurrence of species over larger area
-
AUC(Area Under the Curve) (or ROC): used as the measure if a model is a good model. If it fits the data well;
-
Percent Contribution :measure how important each variable is
-
Permutation Importance: how important the order of adding variables to the model runs
Spatial Regression
- Spatial regression models incorporate the relative location of dependent and independent variables in a regression model to identify the different relationships across space
System Dynamic Models
- Processes that are influenced by space and that influence/modify the space
Spatial Predictive Modeling
- Attempts to describe constraints and influences on where events occur by spatially correlating occurrences with these factors that represent constraints;
- A process for analyzing events through a spatial filter in order to make predictions for event to occur
Spatial Dynamic Models
- Uses identical simple components(cells) to exhibit complex behavior
- Each cell has it state s(i,t) at site i and time t
- Rules for exchanges between sites can also be defined
Agent-Based Models
- An agent represents an independent entity with a set of attributes
- Three characteristics separate the agents apart from the cells:
- Autonomy
- Interaction activity
- Reactivity
All articles in this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 unless stating additionally.
Comment