SSCI-581-Week12
Cartography
Map is communication
Four elements in Communication
- Audience
- Intent
- Format
- Strategy
Types of Maps
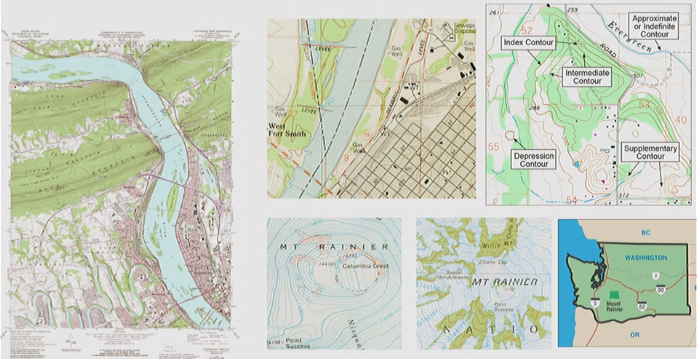
Reference Maps
- General purpose maps
- Emphasize physical environment
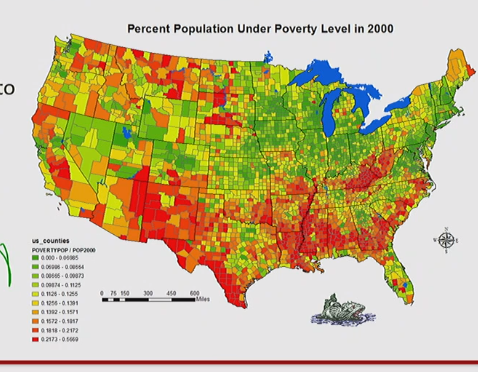
Thematic Maps
- Maps focusing on a particular topic that is tied to location rather than solely location
- Example:
- Choropleth - Quantitative -> Graduated or different colors to show different values
- Choropleth - Qualitative -> Different colors represent different classifications
- Example:
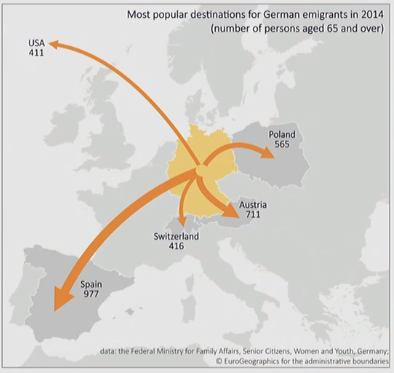
Flow Maps
- Arrows show direction
- Thickness shows value/amount
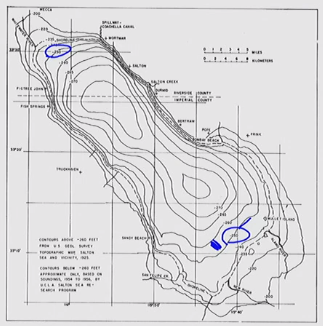
Isoline
- Lines show area of equal value
- Values labeled directly on the line
- Lines can be labeled multiple times
- Used for all types of continuous phenomena: elevation, rainfall, temperature, depth
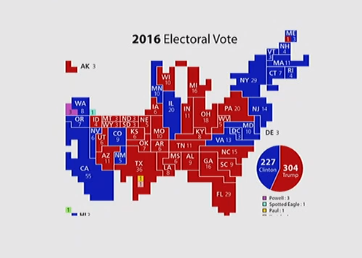
Cartogram
- Map area represent the value, not the actual geography/physical size
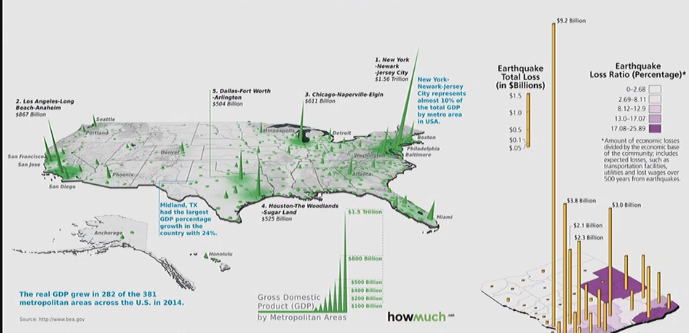
3D Map Models
- 3D visualization of values
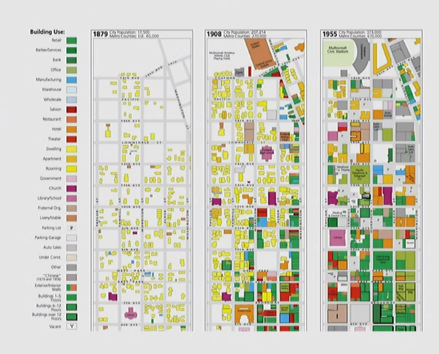
Content of Maps
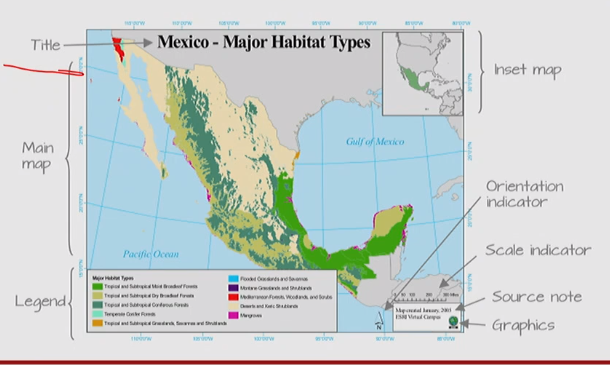
Layout and Elements
- Title
- Inset map
- Main map
- Legend
- Source note
- Graphics
- Orientation indicator (may be not necessary on small-scale maps)
- Scale indicator (Scale bars should not have odd divisions)
All articles in this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 unless stating additionally.
Comment