Lecture12-Note
Semantic Metadata
What is Metadata
- Metadata is information about data
- Metadata is typically
- Manually provided
- Often missing
- Metadata can be automatically captured
- By a sensor or instrument
- By a workflow system
Uses of Metadata
- Facilitate reuse by others
- Support queries on data repositories
- Explain the context for the data in terms of how it was collected or generated
- Enable automated data integration
Types of Metadata
- Data characteristics: Size, statistical properties
- Descriptive metadata: Location, collection, frequency
- Provenance metadata: What workflow was used, what its components were, what the input data was
Metadata Vocabulary
-
A metadata vocabulary is the set of the terms used to describe metadata
-
A metadata standard is a vocabulary that is agreed upon by a community and are adopted for metadata
- Based on its broad applicability and how well it supports uses of the metadata
Metadata from general to specific
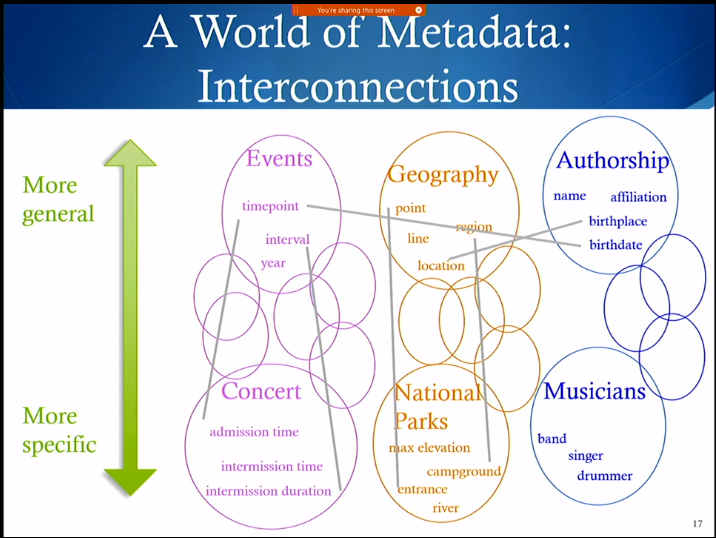
Representing Metadata
-
Metadata captures knowledge about objects in the domain of interest
-
It is important to learn computational concepts for knowledge representation
-
These representations are key to communicate important expertise to collaborating data scientists and computer scientists
Knowledge Representation
- Knowledge is a set of beliefs held by an agent that determine its behavior
- Knowledge representation is a field of artificial intelligence devoted to developing and implementing computer languages to capture knowledge
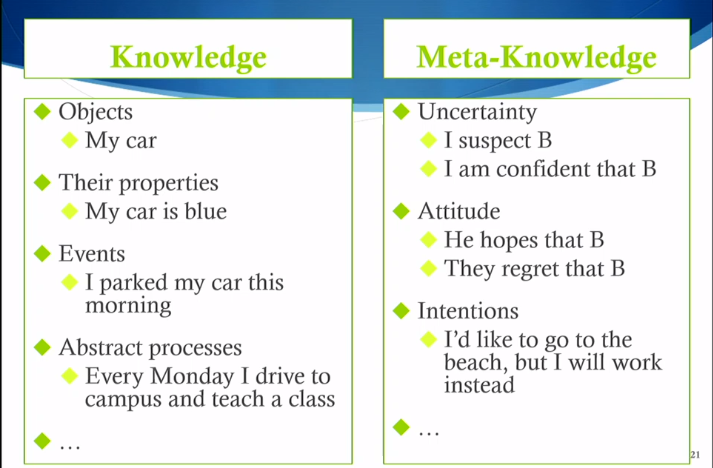
Meta-Knowledge
Descriptive Knowledge

- Note: Properties is about relationship

Knowledge Systems
- Knowledge systems use a knowledge base of beliefs to generate their behavior
- Behavior changes when new beliefs are added
- If they exhibit wrong behaviors/answer, beliefs can be changed to fix them
- They reason: use logical inference over their beliefs to answer queries/deduce new beliefs
- uses a logic system to reason over the beliefs/data in the knowledge base
- Knowledge system uses knowledge base that contains the beliefs, and then uses a logic system (such as knowledge representation system, like a frame system) to reason over beliefs
Reasoning
- Reasoning is done over symbols that make up the beliefs much like calculations are done over numbers
- Reasoning uses a logic system to do inference: a system of general logic rules to deduce new beliefs from initial beliefs in a knowledge base
- Natural deduction is an example of a logic system
Knowledge base
- Symbol are labels that can be used to refer to entities in the world
- Several symbols may exists for the same object
- A knowledge representation language specifies
- Symbols and a notation ofr how to combine the symbols to represent beliefs
- A knowledge base is a set of beliefs and can be used by a knowledge system to generate its behavior
Knowledge Representation System(KRS)
- A knowledge representation system is a logic system that has three components:
- Knowledge representation language: what symbols can be used an how to combine them
- Logic rules: how can the system infer new beliefs given initial beliefs
- Reasoning algorithm: how teh system uses the language and the logic rules
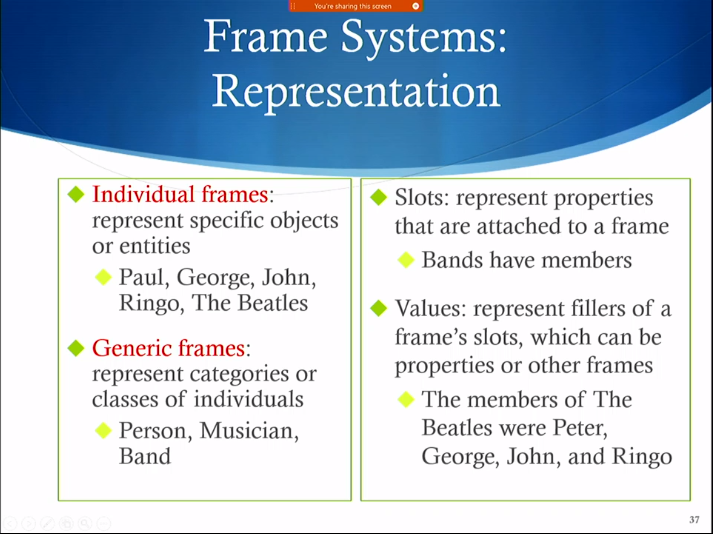
An example of KRS: Frame Systems
- A frame system is a kind of knowledge representation system for descriptive knowledge
- Each class is represented as a frame that captures is main characteristics
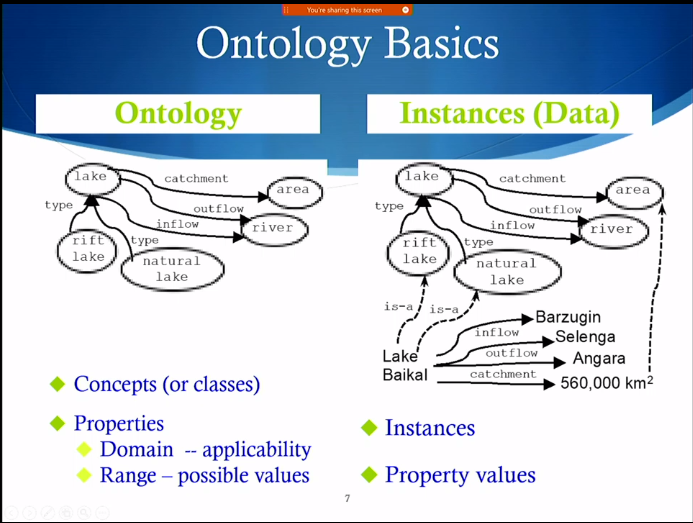
Ontology
- An ontology contains descriptive knowledge about entities of interest in a domain
- A shared conceptualization of the world
- An ontology is typically a collection of generic frames
- Vs. a vocabulary, which is just a set of terms but not organizing them within a hierarchy
- Ontology is a “generic frame only” knowledge representation system
- Ontologies thus have the 3 components and not associated instances/data
Ontology vs. Instances
Knowledge Representation System: Important Characteristics
- Decidability
- Undecidable if it may never return an answer
- Expressivity
- What its formal language can represent
- Soundness
- Whether the logic works as intended
- Computational complexity
- How much computation is required to get an answer
- Explainability
- Whether an understandable proof/explanation is generated
OWL:The Web Ontology Language
- A standard language for the web (like HTML), specifically for authoring ontologies
- Knowledge representation language used to author ontologies - ‘generic frame only’ knowledge representation system - for the web
- Represents descriptive knowledge on the web
- Can result in a more elaborate version of a frame system
- Provides for:
- Language
- Rules
- Reasoning algorithm
Description Logics
- OWL as description logics:
- Knowledge representation language
- Descriptive knowledge
- Description logics - language designed for knowledge representation and reasoning for descriptive knowledge
All articles in this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 unless stating additionally.
Comment