Lecture13-Note
The semantic Web and Linked Data
Linking Ontologies on the Web
- How to Link Ontologies:
- (1) Through URLs
- (2) Mapping Terms
Nesting metadata within webpages
RDF: The Resource Description Framework
-
Semantic triples are beliefs written as triples of the web:
- < object property value> or < subject predicate object >
-
Example:
-
< Leonardo painted LaMonaLisa >
-
< Shakespeare wrote Hamlet>
-
< Bob isInterestedIn LaMonaLisa>
-
RDF Syntax(RDFS), a simple logic language, is used to write triple, and can include instances/individual frames
- Owl can be used to write them too, but used for ontologies on the web (generic frames/only classes)
-
Can be used to make graphs of links on the web
-
Allows for reasoning (i.e., you can query wikidata)
Triples on the web
- Triples can be written on the web using:
- Knowledge representation language e.g., OWL
- typically only for generic frames/classes
- also allows for beliefs with more complicated relations than in triple
- Simpler logic language e,g, RDFS
- also allows for individual frames/instances
- Knowledge representation language e.g., OWL
Ontologies vs Taxonomies vs Vocabularies
- Vocabularies: a set of terms to describe the metadata
- Taxonomies: a hierarchical organization of terms
- Ontologies: formal taxonomies defined using logic
- Mathematical logic used to define what the hierarchies mean
- Subclasses imply containment of instances
- Instances of a class have all the properties of the class
- Logic constraints
- Example: all humans have exactly one biological mother
- Mathematical logic used to define what the hierarchies mean
Provenance
Defining Provenance
- Each time the workflow is executed, the system records the provenance of the results: what workflow was used, what its components were, what the input data was, and what values were assigned to the parameters.
- Provenance can be part of metadata.
- provenance for a resource(e.g, data, document, etc.) is a record that describes entities and processes involved in producing and delivering or otherwise influencing that resource.
The Importance of Provenance
- Provenance fosters trust
- Provenance provides a critical foundation for assessing authenticity and allowing reproducibility
Representing Provenance
- PROV is used to represent Provenance
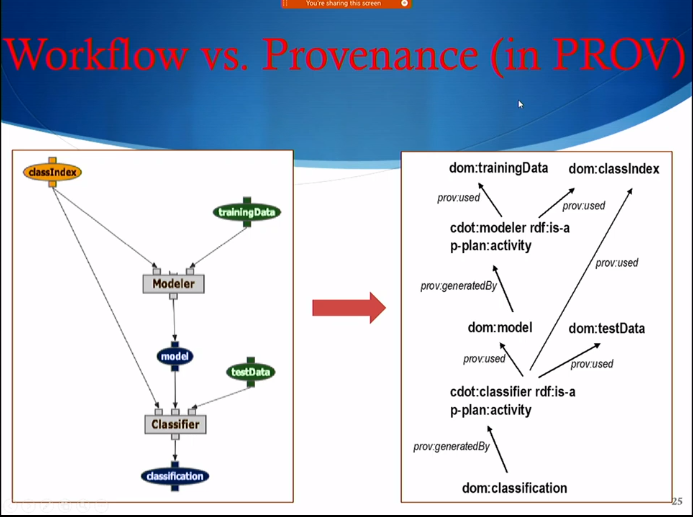
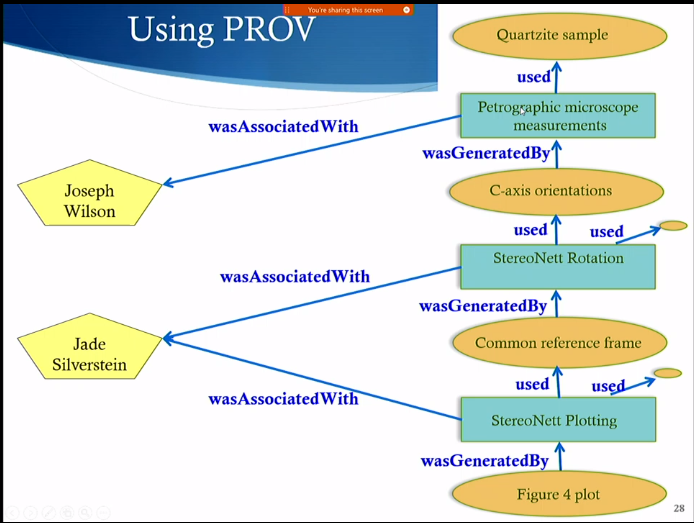
Three Uses of Provenance
- Provenance as Process(Computing Steps, Actions, etc)
- Provenance as Resources themselves
- Provenance as Attribution (to people, institutions, etc)
Publishing Data
Problem with current practice
- Data is often not made available in publications. Lack of reproducibility.
- Data made available through investigator’s URL, but URL does not resolve.
Best practices to make data accessible
Data Citation
- Data repositories and journals often specify how to cite data
- Unique persistent Identifiers:main types of Unique Identifiers include:
- Uniform Resource Locator (URL): minimal effort to create. No guarantee of persistence. Should not be used in papers.
- Persistent URL (PURL): the same PURL can be resolved to different web address over time. It is easy to create your own PURLs, just remember to update whenever you move the data.
- Digital Object Identifier (DOI): DOI can only be issued by a DOI authority. Data repositories can issue DOIs for data.
Accessibility
- Manual Accessibility
- Machine Accessibility
General metadata & Domain Specific meta data

Publication in a shared repository
Choose a License for data
- Recommended: CC-BY and CC0
Publishing Software
Software citation
- As with data, use a persistent unique identifier (PURL or DOI)
- How to cite the software:
- With an in-text pointer as you would cite any other paper (recommended)
- With an in-text pointer in the “Acknowledgments” section
Choosing an License for Software
- Copyright: automatically applied to software when it is created to grant the creator exclusive rights as an intellectual property
- Open source license: reduce constraints and enable software developers to make their source code available to public.
Ideal data science reports
- Data: available in a public repository, including documented metadata, a clear license specifying conditions of use, and citable using a unique and persistent identifier.
- Software: available in a public repository, with documentation, a license for reuse, and a unique and citable persistent identifier.
- Provenance: documented for all results with a workflow sketch and with a provenance record.
Metadata standards:
- Friend-of-a-Friend (FOAF): focus is describing people and their relationships.
- OWL Time: a proper ontology with detailed constraints about classes and properties.
- The Gene Ontology (GO): focus is genomic information.
How do standards come about? - Standards organizations
- Industry-led
- A PhD thesis
- A community
The World Wide Web (W3C) Consortium:
- Focus on web standards, such as HTML, XML, OWL, RDF, etc.
- Incubators analyze state of the art, and generate proposals that become the charter of working groups.
- Working groups have a finite amount of time to accomplish their charter and generate a standard.
Need for standards: since there are many uses of provenance: - Open information systems
- Science applications
- Business practices
All articles in this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 unless stating additionally.
Comment