SSCI-581-Week4
Spatial Representation and Power
The Authority of Maps
Maps are read as authorities; they are difficult to create and mapmakers have technical skill; people trust what they see in maps
But mapmaking is not objective; many choices must be made. What to map and how to map it are choices
Culture is embedded in maps, such as ideas about the nature of land and human society
Propaganda(宣传;鼓吹) maps are extreme examples
Land Areas and Epistemoloty
We see maps as evidence of physical world
The appear ...
SSCI-581-Week3
Scale
The Concept of Scale
Scale is the size or extent of something
The temporal scale is the length of time
The spatial scale si the physical size or extent
Spatial Scale
1. Cartographic Scale
The ratio of the distance on the map to the distance in the physical world
Three types of Cartographic Scale:
Verbal (word) scaleGraphic (scale bar)Representative fraction (RF)
WordS describe UNITS of distance on map compare to UNIT of distance in physical world
Rarely used outside printed paper map ...
Lecture6-Note
Correlation
What is Correlation
Two variables are correlated (associated) when their values are not independent
Probabilistically speaking
Examples:
When people by chips they are very likely to buy beer
When people have yellow fingers, they are very likely to smoke
Variables that are predictive
Some variables are predictive because they are correlated with other target variables
Smoking and coughing are predictive variables for respiratory disease
Cause and Effect
A variable v1 is ...
lecture5-Note
Type I Error
false positive, "rejected the null" but there is no difference
Rejecting a true null hypothesis
Also known as false positive or α\alphaα error
Concluding there is a difference when there actually is none
Easy to control
Decide the probability α\alphaα in advance for a given test
The standard cutoff is 0.05, meaning there is a 5% chance of a Type I Error
Type two Error
false negative, "failed to reject" bull there is a difference
Failing to reject a fa ...
SSCI-581-Week2
Geography
The study of the Earth and its systems. inhabitants, and processes
Physical Geography: the study of the Earth’s environmental processes
Human Geography: the study of people and how their activities vary
Environmental Studies: the systematic study of human interactions with the environment (to solve complex problems)
Geomatics: the collection, distribution, storage, analysis, processing, and presentation of geographic data or information
Urban/Regional Geography
Cartography
The study ...
SSCI 581 Week1
What Is GIS?
In technology part, GIS is the abbreviation of Geographic Information Systems
Computer-based (hardware & software) system that:
Create locationally referenced data
Stores and organizes locationally referenced data
Performs spatial analyses
Creates visualizations, usually in map form (but also tables, graphs, dashboards)
In theory part, GIS is the abbreviation of Geographic Information Science
Theory behind how to solve spatial problems and how to implement GISystems
The stud ...
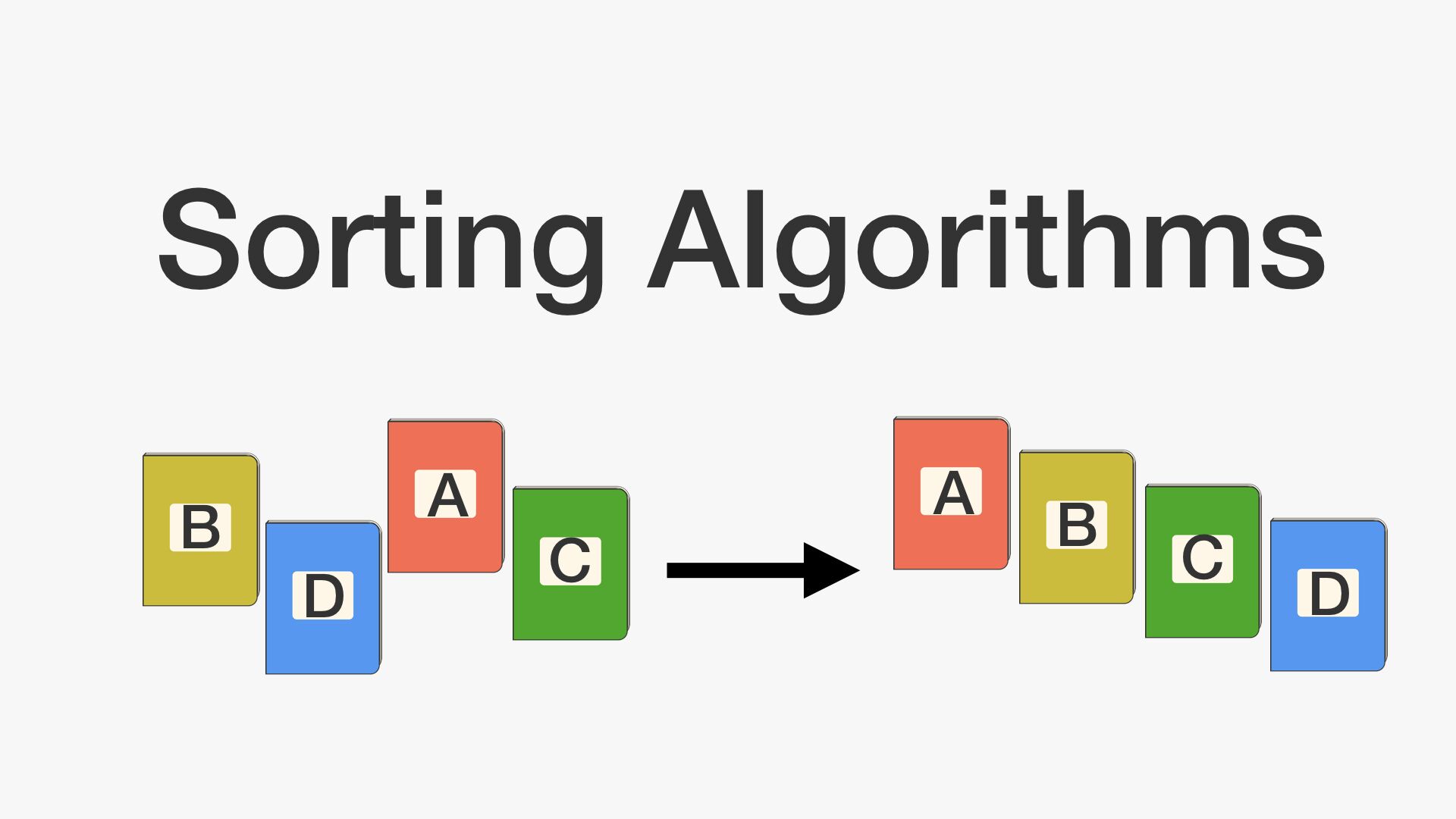
Sort Algorithms
Selection Sort
Selection sorting a list of N items:
Find the smallest item
Move it to the front
Selection sort the remaining N-1 items (without touching front item!).
Selection sort
Code with Java:
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829// Background: Using Selection to sort a String Array// 1. Find the Smallest itempublic static int findSmallest(String[] x, int start){ int smallestIndex = start; for(int i = start;i<x.length;i++){ int cmp = x[i].compareTo( ...
Lecture4-Note
Logic and Probability For Statistics
Descriptive Statistics
What is a Mean (M) ?
Measurement of central tendency
Mathematical midpoint (average) of a data set
Standard Deviation (SD)
SD=∑(X−X‾)2NSD = \sqrt\frac{\sum(X -\overline{X})^2}{N}
SD=N∑(X−X)2
Measurement of variability
How variable is the data
How close to the mean is a given value
Target of descriptive statistics:
Descriptive statistics can be run on the entire target and take a sample is the usually method.
Use ...
Lecture2 Note
Lecture2 Note
Programs Implement Functions
Definition: Function is a type of procedure or routine.
Example of function:
Inputs and Outputs of Programs
Clear what are the inputs of the program and what are the outputs of the program.
Program Parameters
Parameters are the special inputs, which are the necessary context for the program to run. (But not every program needs prameters)
Parameters can be chose by youself or set the program to choose a random parameter or optimize the parameter b ...
Lecture1 Note
lecture1 Note
What is Data?
Data information that is pocessable by Computer
Information is in ditial form
A program can read and analyze the information
Accessible Data
Right to access to the data
Procedure to obtain or use the data
Option 1: Locally
Option 2: Remotely
API
An API is a doucemnt that specifies what queries are possible and their format, and the format of the responses.
## Licenses for Data
Creative Commons provides licenses for data.
Followings are details ...